Introduction
Phishing is a type of cyberattack where attackers pretend to be trusted organizations. They trick people into giving up sensitive information like usernames, passwords, or credit card details. Phishing can happen through emails, text messages, or phone calls. These scams lead victims to harmful websites or ask them to download dangerous software. Phishing uses human trust, making it a major threat to online security. Learning how to recognize phishing attempts is crucial to avoid phishing scams and stay safe online.
Phishing attacks affect both individuals and businesses. For individuals, phishing scams can cause identity theft, loss of money, and stress. Phishing is responsible for 15% of data breaches in 2024, costing businesses about $4.88 million per breach. Phishing attacks can cause big financial losses and long-term harm. For businesses, phishing can damage their reputation and customer trust. Famous cases like the phishing attack on Hillary Clinton’s 2016 campaign show how phishing scams can expose sensitive data. This shows why phishing prevention is important and why we need to stay alert to online fraud.
In this blog, you’ll discover how to spot phishing emails, avoid falling for phishing scams, and protect yourself from these attacks. You’ll find helpful tips on recognizing phishing attempts, along with advanced online security strategies to keep you safe. By the end of this guide, you’ll have the knowledge and tools to secure your online information.
Understanding Phishing
What is Phishing?
Phishing is when cybercriminals pretend to be trusted organizations to trick people into giving up sensitive information like usernames, passwords, credit card numbers, and more. These scams often come in emails, text messages, or phone calls. The attackers make people feel they need to act quickly, pushing them to click harmful links or share personal details. Learning how to recognize phishing attempts is the best way to avoid phishing scams.
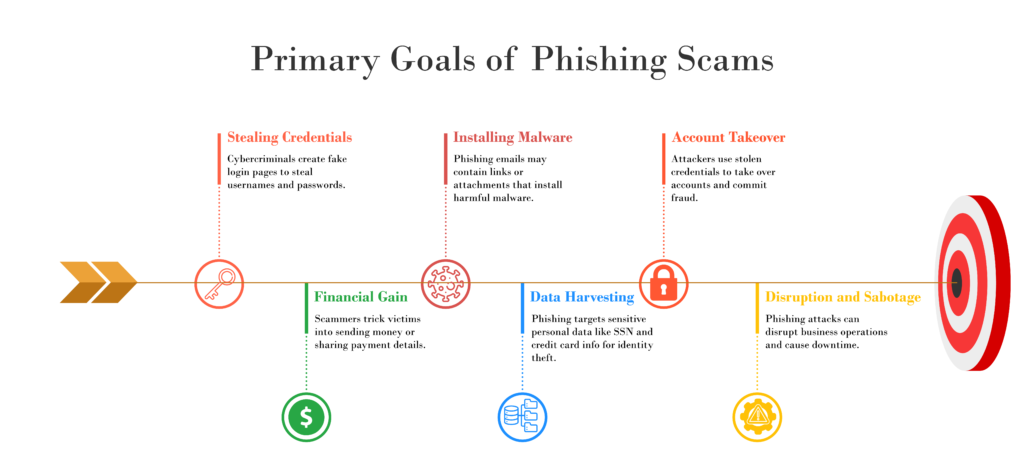
Primary Goals of Phishing Scams
Understanding the goals of phishing scams is key to phishing prevention. Cybercriminals have clear aims when they carry out phishing scams. Knowing these goals helps you protect your online security. Here are the main goals of phishing scams:
- Stealing Credentials: A major goal of phishing is to steal login credentials. Cybercriminals create fake login pages that look like real websites. Victims are tricked into entering their usernames and passwords. This is why learning how to recognize phishing emails is crucial to prevent online fraud.
- Financial Gain: Many phishing scams aim to steal money. Scammers use fake invoices or urgent requests to make people send money or share payment details. This is a common phishing tactic that targets both individuals and organizations. Phishing prevention tips include staying alert to these methods to protect from identity theft protection risks.
- Installing Malware: Another goal of phishing is to install malware. Phishing emails or texts may have dangerous links or attachments. Clicking these can install malware that steals data or takes control of the system. Malware prevention should be part of any online security plan.
- Data Harvesting: Phishing scams also target sensitive data like Social Security numbers and credit card details. Cybercriminals sell this stolen data on the dark web or use it for identity theft. Knowing how to identify phishing emails that ask for personal info is important for protecting your privacy. Phishing prevention tips include not sharing personal details online unless you’re sure the website is safe.
- Account Takeover: Phishing can also be used to take over accounts. Once attackers steal login details, they can access financial or business accounts. This can lead to fraud or data breaches. Using password security best practices, like two-factor authentication (2FA), helps prevent this.
- Disruption and Sabotage: Some phishing attacks aim to disrupt business by damaging systems or networks. These attacks can cause downtime and loss of work. Cybercrime prevention strategies should include staying alert to phishing scams that could harm operations. Recognizing email scam warning signs can help reduce these risks.
Types of Phishing Scams
Phishing scams come in different forms. Each type uses different methods to trick people. Knowing the types of phishing scams helps protect yourself from these threats. Here are the most common types:
- Email Phishing
Email phishing is the most common form of phishing. Attackers send fake emails that look like they come from trusted organizations. These emails often contain harmful links or attachments that can steal personal information or install malware. Recognizing these types of phishing emails is key to online phishing prevention. - Spear Phishing
Spear phishing is a more targeted attack. It focuses on specific people or companies, using personal details to make the scam seem real. These emails often mention the victim’s name or job. Spear phishing can be very harmful, which is why phishing prevention is important in every organization. - SMS Phishing (Smishing)
Smishing is phishing through text messages. Attackers trick people into clicking harmful links or giving out personal information. For example, they may say you won a prize and ask you to click a link. Knowing how to protect from phishing scams through text is important for online security. - Voice Phishing (Vishing)
Vishing uses phone calls to steal personal information. Attackers often spoof caller ID to look like trusted organizations. They create a sense of urgency to get victims to share their data. Phishing prevention strategies should always include knowing how to handle suspicious phone calls. - Whaling
Whaling is a type of spear phishing that targets high-level individuals like executives. These attacks are highly customized, aiming to steal money or sensitive data. Cybercrime prevention strategies must include protecting top executives from these social engineering scams. - Clone Phishing
In clone phishing, attackers copy real emails from trusted organizations but add harmful links or attachments. The goal is to trick victims into thinking they are dealing with a legitimate message. Clone phishing is common in email security, so always check emails that seem too familiar. - Website Phishing
Website phishing creates fake websites that look like real ones to steal personal information. These fake sites often come from links in phishing emails or text messages. Recognizing website phishing is crucial to avoid online fraud and protect your data. - Social Media Phishing
Social media phishing happens when attackers impersonate real accounts on platforms like Facebook or Instagram. They trick users into giving out personal details or clicking on harmful links. Always verify accounts before sharing personal info on social media. - Business Email Compromise (BEC)
BEC is a sophisticated phishing attack targeting businesses. Attackers impersonate executives or partners to trick employees into sending money or sensitive data. Phishing prevention in the workplace includes training and email security tips to catch these scams. - Malicious QR Codes
Malicious QR codes lead users to fake websites when scanned. Attackers place them in public areas or send them through phishing messages. Always be careful when scanning QR codes from unknown sources to avoid phishing scams.

Anatomy of a Phishing Scams
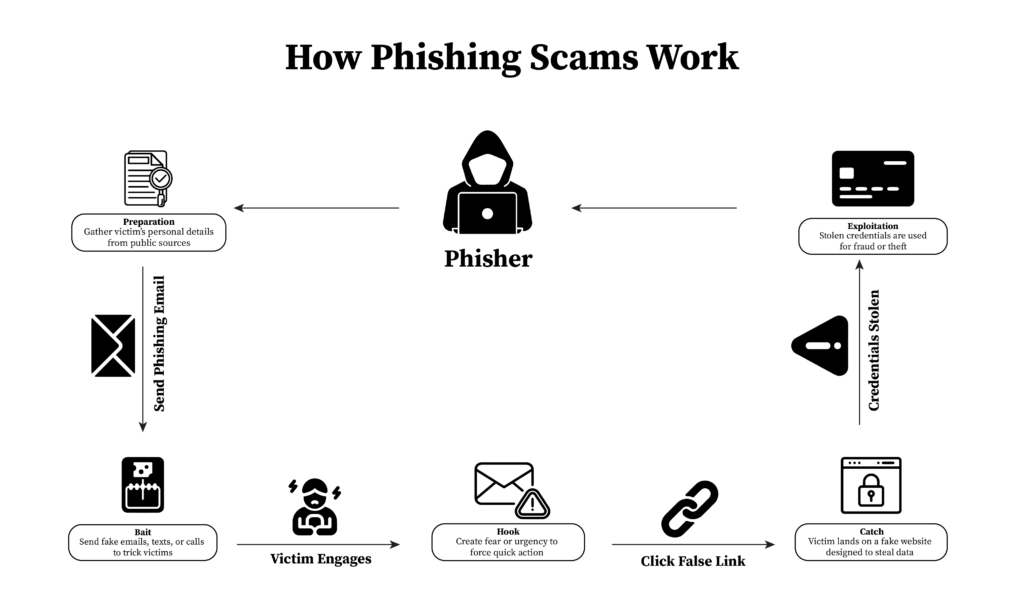
Phishing scams are designed to trick people into sharing sensitive information. Understanding how phishing scams work is key to phishing prevention. Here’s a detailed look at how phishing scams happen, the tricks used, and the technology behind them.
How Phishing Scams Work
- Preparation: Attackers gather information from social media and public sources. They use this to make their messages look real. Recognizing phishing attacks early can help you avoid phishing scams.
- Bait: The attacker sends an email or message that looks like it’s from a trusted source, like a bank. The message asks you to click a link or open an attachment. Phishing email examples often ask you to verify your account to steal your details. Phishing prevention means being careful with messages that seem too urgent.
- Hook: The phishing message creates fear or urgency, pushing you to act fast. For example, it may warn your account will be locked unless you act quickly. Phishing prevention tips suggest checking the message carefully before clicking any links.
- Catch: If you click on the link, you’re taken to a fake website. It looks real, but it’s designed to steal your login information or install malware. Phishing prevention includes checking URLs and making sure websites are secure.
- Exploitation: With stolen credentials, attackers can access your accounts, leading to identity theft or financial loss. Protecting personal information online is important to avoid phishing scams.
Psychological Tricks Used by Phishers
Phishers play on emotions to trick victims. Common tricks include:
- Fear: Phishing emails often threaten consequences, like account suspension, to get you to act quickly.
- Urgency: Phishers push you to act fast and ignore normal safety steps. Curiosity: Some messages try to get you to click by offering interesting deals.
- Greed: Phishers promise rewards to make you give up personal information.
Technology Exploits
Phishing uses tech tricks to fool you:
- Fake websites: These sites look like real ones to steal your login information.
- Malicious links: Phishing messages have links that lead to harmful websites or install malware.
- Spoofed emails: Attackers send emails that look like they come from trusted sources to trick you into clicking dangerous links.
By knowing how phishing attacks work, including the psychological tricks and tech methods used, you can better protect yourself. Phishing prevention steps like checking email addresses, URLs, and using strong passwords can keep you safe from online phishing.
How to Recognize Phishing Scams
Recognizing phishing scams is very important to protect your personal information and online security. Phishing can happen through emails, websites, text messages, and even phone calls. Here is how you can spot and avoid phishing scams on different platforms.
1. Recognizing Phishing Emails
- Suspicious Email Addresses: Always check the sender’s email address. Look for fake domains or strange characters. For example, “paypa1.com” instead of “paypal.com” is a warning sign of phishing.
- Generic Greetings and Language: Phishing emails often say things like “Dear Customer” instead of your name. They may also use urgent language like “Immediate action required!” or “Your account has been compromised.”
- Poor Grammar and Spelling: Be careful of emails with bad grammar, misspelled words, or wrong punctuation. These are common signs of phishing.
- Unexpected Attachments or Links: Be careful with unexpected attachments or links. Hover over links to see where they lead before clicking. This helps you avoid phishing scams.
- Too Good to Be True Offers: Emails saying you’ve “won $10,000!” are often scams to steal your information through phishing scams.
2. Recognizing Phishing Websites
- URL Red Flags: Always check the website URL. If you see a small change, like “secure-paypal.com” instead of “paypal.com,” it could be a phishing site.
- Lack of HTTPS: Real websites have HTTPS and a padlock symbol. If these are missing, the site might be a phishing scam.
- Poor Website Design: Phishing websites may have bad graphics, broken links, or messy layouts. They are easy to spot if you know what to look for.
- Absence of Privacy Policy or Contact Info: Trusted websites usually have clear privacy policies and customer contact info. If these are missing, it’s likely a phishing site.
3. Recognizing Phishing Links
- Hovering Over Links: Always hover over links in emails or texts to see where they go. If the link doesn’t match the real site, it’s a phishing link.
- Spoofed URLs and Homograph Attacks: Be careful of phishing websites that use similar-looking letters, like replacing “o” with a zero. These tricks are common in phishing scams.
- Shortened Links: Phishing scams often use shortened links (like bit.ly) to hide the real destination. Be careful with these links.
4. Phishing in Text Messages (Smishing)
- Unsolicited Texts Requesting Personal Information: Be careful of unexpected text messages asking for personal info, like bank numbers or passwords. These are usually smishing scams.
- Urgent Calls to Action: Smishing texts may say your account is locked and ask you to click a link or call a number. These are signs of phishing.
5. Recognizing Phishing Calls (Vishing)
- Suspicious Calls Asking for Sensitive Information: Be careful of unexpected calls asking for personal details, like credit card numbers. These could be vishing attacks.
- Fake Tech Support: Be cautious of calls claiming to be tech support, especially if they want remote access to your computer or ask for personal info. This is a common phishing trick in vishing scams.
6. Phishing on Social Media
- Fake Social Media Profiles and Posts: Phishers create fake social media accounts pretending to be real companies or celebrities. They trick you into sharing info or clicking on bad links.
- Phishing via Direct Messages: Be cautious of unexpected messages on Facebook, Instagram, or LinkedIn asking for personal information. These are often phishing attempts.
- Deceptive Contests and Offers: Fake contests or giveaways that ask for personal info are often phishing scams.
7. Recognizing Phishing in Calendar Invites and Other Invitations
- Fake Calendar Invitations: Be careful of calendar invites with links or attachments that look suspicious. Always verify the sender before accepting any invites.
- Suspicious Event Notifications: Invitations for events or webinars from unknown sources asking for personal details are likely phishing attempts to steal your data.
By watching for these signs of phishing, you can avoid scams on different platforms. Recognizing phishing emails, websites, links, and other tricks is key for phishing prevention and online security.
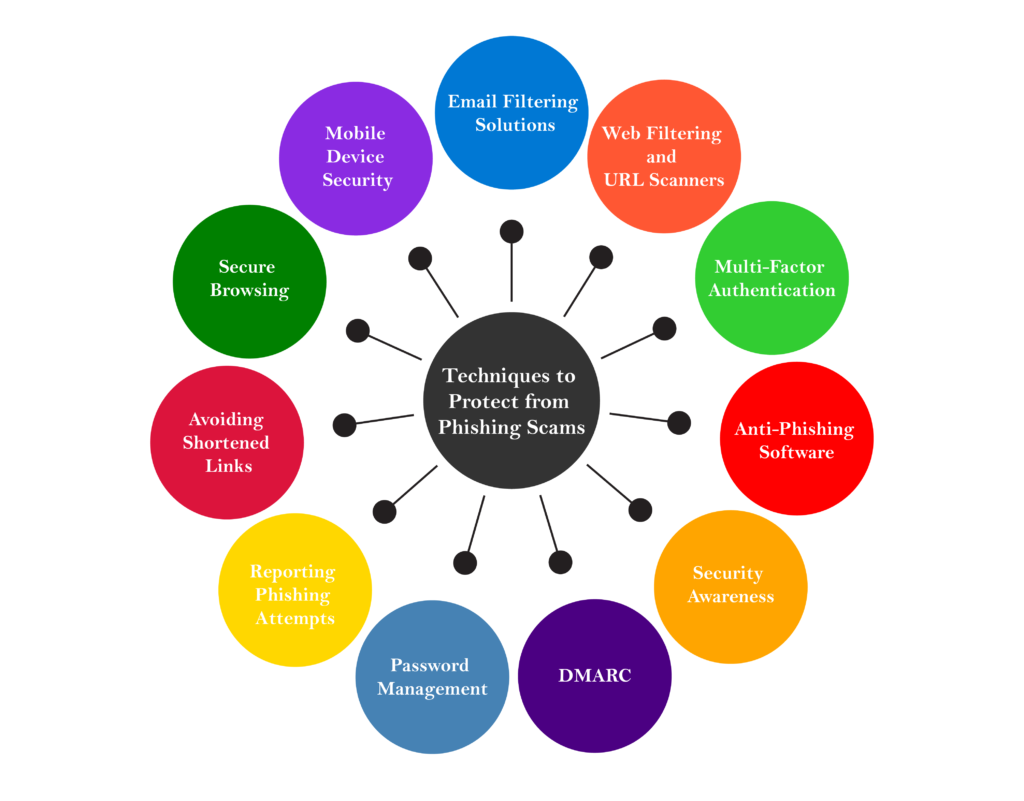
Tools and Techniques to Protect Yourself
Phishing attacks are getting harder to spot. It is important to use the best tools and methods to protect yourself. Here is a guide on the main tools and techniques to keep you safe from phishing scams.
1. Email Filtering Solutions
- Email filtering tools stop phishing emails before they reach your inbox. These tools check incoming emails for suspicious addresses and harmful attachments.
- Popular Tools: Microsoft Defender for Office 365, Proofpoint, Barracuda Essentials
- How They Work: These tools use algorithms, blacklists, and machine learning to detect phishing emails.
2. Web Filtering and URL Scanners
- Web filtering tools block phishing websites and warn you about unsafe URLs. These tools scan web traffic to keep you safe from phishing sites.
- Popular Tools: URLScan.io, VirusTotal
- Best Practice: Always scan unknown URLs before clicking, especially if they come from unexpected sources.
3. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- MFA adds extra security to your online accounts. Even if attackers get your login details from phishing, MFA needs a second step to let them in.
- Benefits: MFA lowers the risk of phishing attacks by making sure stolen credentials alone can’t give access to accounts.
4. Anti-Phishing Software
- Anti-phishing software helps detect and stop phishing across all platforms. These tools offer real-time protection.
- Examples: Mimecast, Netcraft, Avanan
- Features: These tools scan links, attachments, and provide real-time threat updates to protect from phishing.
5. Security Awareness
- Training Teaching employees how to spot phishing attempts is very important. It helps them know how to react properly.
- Implementation: Run fake phishing attacks to test employee awareness and improve training.
6. Domain-Based Message Authentication DMARC
- Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance (DMARC) stops email spoofing by making sure only trusted senders can use your domain.
- Benefits: DMARC improves email security and stops phishing attacks that use fake email addresses.
7. Password Management
- Use strong passwords with phishing-resistant MFA to keep your accounts safe. Tools like FIDO authenticators make logging in easy and secure.
- Recommendation: Regularly change your passwords and use a password manager to store them safely.
8. Reporting Phishing Attempts
- Encourage everyone to report phishing emails to IT teams.
- Benefits: Reporting phishing helps track scams and improve defenses for the future.
9. Avoiding Shortened Links
- Shortened links (like bit.ly) can hide where they really lead. Be careful and scan these links before you click them.
- Recommendation: Always check shortened links with a URL scanner to avoid phishing traps.
10. Secure Browsing
- Practices When browsing online, make sure the website is secure by checking for HTTPS. This protects your sensitive data from phishing.
- Best Practice: Never enter personal details on websites that are not secure.
11. Mobile Device Security
- Use mobile security apps to stop phishing sites while browsing the web. Apps like the Netcraft Mobile App protect you from phishing and malware.
- Example Tools: Netcraft Mobile App stops phishing scams and unsafe websites.
By using these tools and techniques, you can protect yourself from phishing attacks. These strategies will lower the chances of identity theft and data breaches, making your online experience safer.
Advanced Strategies to Avoid Phishing Scams
1. Email Authentication Protocols
Email authentication protocols help check if an email is from a real sender and stop phishing attacks. The three main protocols are:
- Sender Policy Framework (SPF): SPF lets domain owners decide which IP addresses can send emails for them. This stops phishing by checking if the sender’s IP address is on the approved list.
- DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM): DKIM adds a digital signature to emails using public-key cryptography. This signature proves the email is real and that nothing has changed in the email.
- Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance (DMARC): DMARC works with SPF and DKIM to decide what to do with emails that fail checks. It also gives reports to watch for phishing.
Using these main protocols helps block phishing and improves email security.
2. User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA)
UEBA tools look at how users act to spot unusual behavior. For example, if someone logs in from a different place or gets sensitive data, UEBA can alert you. These tools help stop phishing scams by finding abnormal actions.
3. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA adds extra security to your accounts. If attackers steal your login info from phishing, they still need a second step to get in. This could be a code sent to your phone or an app. MFA makes phishing harder for attackers and protects your accounts.
4. Use Secure Web Gateways and DNS Filtering
Secure Web Gateways (SWG) and DNS filtering stop users from going to phishing websites. SWGs block bad websites from loading, while DNS filtering stops users from connecting to phishing domain names. These tools keep you safe from phishing websites.
5. Leverage Machine Learning and AI
Machine learning and AI look at data in real-time to find phishing attacks. They can spot patterns in emails, URLs, and sender behavior that are common in phishing. As these systems learn, they get better at stopping new phishing threats.
6. Advanced Email Filtering Solutions
Using advanced email filters is important for finding phishing emails. These tools use machine learning to look for patterns in emails. They can spot phishing signs like fake email addresses or dangerous attachments and stop the emails before they reach you.
7. Conduct Regular Security Awareness Training
Training employees to spot phishing attempts is very important. Simulated phishing tests help check how ready employees are. Training helps workers stay alert and spot phishing scams, making them a key part of your defense.
8. Regular Software Updates
Updating software regularly is important for security. Phishing often uses weaknesses in old software. Keep your system, browser, and email updated with security fixes to lower the risk of phishing attacks.
9. Strong Password Policies
Strong passwords help stop phishing attacks. Make sure users create hard-to-guess passwords and change them often, like every 90 days. Using password managers can help make and store strong passwords, so you don’t fall for phishing scams targeting weak ones.
10. Monitor for Advanced Phishing Techniques
Stay aware of new phishing tricks like Adversary-in-the-Middle (AiTM) attacks, HTML smuggling, and AI-generated phishing emails. Regularly check your security and adapt to new phishing scams. By staying updated on phishing techniques, you can strengthen your defenses.
By using these advanced tools and techniques, you can greatly lower the risk of falling for phishing attacks. These steps help keep individuals and organizations safe from phishing scams.
What to Do If You Fall for a Phishing Scam
If you fall for a phishing scam, stay calm. Acting fast can help protect you from more harm. Follow these steps to stay safe.
Immediate Steps
- Disconnect from the Internet
First, disconnect your device from the internet. This stops the phishing scam from spreading. If you use Wi-Fi, turn off the router or disconnect from the network. For wired connections, unplug the internet cable. This helps prevent more damage from the phishing attack. - Change Compromised Passwords
Change the passwords for any accounts that may be affected. This is very important for banking, email, and social media accounts. If you use the same password on different accounts, change those too. Turn on two-factor authentication (2FA) wherever you can for extra protection. - Alert Your Bank or Credit Card Provider
Call your bank or credit card provider right away. Tell them about the phishing attack. They can watch your accounts for any strange transactions and help you freeze your account or get new cards. This step is very important to protect your money after a phishing attack.
Reporting Phishing Attacks
- Report to Email Providers
Forward any phishing emails you got to your email provider, like Gmail or Yahoo. This helps the provider block the sender and stop similar attacks. Reporting phishing emails helps protect others from getting tricked. - Contact Cybersecurity Authorities
Report the phishing attack to authorities like the Federal Trade Commission (FTC). This helps track phishing scams and warn others. It also helps stop phishing from spreading across the internet. - Notify Affected Organizations
If the phishing scam pretended to be a real company, like a bank, let them know. This helps the company warn other customers and stop more phishing attacks.
Recovering from Identity Theft
- Protect Your Credit Score
Put a fraud alert on your credit reports by calling the credit bureaus, like Experian, TransUnion, and Equifax. This will make creditors check your identity before opening new accounts. You can also freeze your credit to make it harder for anyone to get your information. - Monitor Sensitive Data
Check your bank statements and credit reports often for any transactions or new accounts you didn’t open. You can use free services like Credit Karma or AnnualCreditReport.com to help keep track of your credit and spot any fraud fast. - Use Identity Theft Protection Services
Consider using identity theft protection services. These services can help you watch your personal information and let you know if anything strange happens. They can also help you recover quickly if someone uses your information in a phishing attack. - Educate Yourself and Stay Vigilant
Learn about phishing scams and how they work. Keep up with the latest scams. Share this knowledge with your friends and family to help protect them too. Staying alert and informed helps you avoid future phishing scams.
By following these steps, you can reduce the damage from a phishing attack and keep your online safety in check. The quicker you act, the better chance you have to stop further harm caused by phishing scams.
The Future of Phishing
Phishing is changing. Cybercriminals are using new tools like AI and deepfakes. They also use tricks to manipulate people. Cybersecurity is using AI, behavior analysis, and many protection layers to fight back. Here’s what’s coming in the future of phishing.
Advanced Phishing Techniques
1. AI-Generated Phishing Campaigns
Cybercriminals use AI to make phishing emails look real. They study social media and public records to make emails seem personal. These emails are hard to spot and can reach many people at once.
2. Deepfakes and Voice/Video Phishing
Deepfake tech helps criminals create fake videos and voices. These could look like a boss or family member asking for sensitive information. Deepfakes make phishing harder to detect.
3. Phishing-as-a-Service (PhaaS)
Phishing-as-a-Service gives attackers easy access to phishing kits. These kits can bypass multi-factor authentication (MFA) and make attacks easier to run. This helps even new criminals steal login details.
4. Sophisticated Evasion Techniques
Phishers use new tricks to hide their attacks. They may put malicious links in email attachments or use shortened URLs. They hide phishing content in cloud storage, making it harder for systems to find them.
How Cybersecurity is Evolving to Combat Phishing
AI and Machine Learning-Based Detection
Cybersecurity tools now use AI and machine learning to spot phishing. These tools look for strange activity and learn new ways to fight phishing over time.
Behavioral Analysis and Anomaly Detection
Security systems track how users interact with emails and websites. They look for unusual actions, like clicking suspicious links. These systems can catch attacks before they happen.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Beyond
MFA helps stop phishing, but attackers find ways to bypass it. To fight this, new protections like biometric authentication and hardware tokens are being added. These make accounts safer.
Enhanced Email Filtering and Detection
Email security is getting better. AI-powered tools now check the content, sender, and context of emails. This makes it harder for phishing emails to reach you.
Security Awareness Training and Simulated Phishing Attacks
Training helps people spot phishing scams. Many companies run simulated phishing attacks to teach employees what to look for. This makes workers more aware and ready to protect themselves.
Phishing is getting smarter, but cybersecurity is getting stronger. With new tools and awareness, we can stay ahead of these attacks.
FAQs
1. What is phishing in simple terms?
Phishing is when attackers act like trusted companies to trick you into giving them private information like passwords or credit card numbers.
2. Can antivirus software prevent phishing?
Antivirus software can block some phishing attempts and malware. But it’s not enough. You need other tools like email filtering and always stay alert.
3. What should I do if I receive a phishing email?
If you get a phishing email, don’t click on links or open attachments. Tell your email provider, delete it, and change your passwords if you clicked.
4. Is using a VPN effective against phishing?
A VPN keeps your online connection safe but doesn’t stop phishing attacks. Be careful and use other tools to avoid phishing.
Conclusion
In conclusion, phishing scams are a huge threat to online safety. These scams trick people into giving away important information like passwords, credit card numbers, or personal details. Phishing can happen through emails, text messages, phone calls, and fake websites. It is very important to learn how to spot phishing attempts so you don’t fall for them.
Phishing attacks have different goals. Some try to steal login credentials, while others aim to steal money or install malware. Knowing these goals helps protect your online information. The most common types of phishing are email phishing, spear phishing, and smishing. Being aware of these scams and using the best tools can keep you safe.
To stay safe, use tools like email filters, multi-factor authentication, and anti-phishing software. Always check URLs, email addresses, and attachments before clicking. Be careful of fake messages or websites asking for personal info. With the right knowledge and precautions, you can protect yourself from phishing scams. Always stay alert and use security tools to keep your information safe online.


